From nerve function to red blood cell formation, vitamin B12 plays an essential role in many of your body’s processes. Vitamin B12 — also known as cobalamin – is crucial for nerve tissue health, brain function and the production of red blood cells. Unlike other, more straightforward vitamins, there are a whopping eight different B vitamins.
- Thiamin (B1)
- Riboflavin (B2)
- Niacin (B3)
- Pantothenic acid (B5)
- Pyridoxine (B6)
- Biotin (B7)
- Folic acid (B9)
Table of Contents
Why you need vitamin B12
- Forming healthy red blood cells
- Normal brain function
- Central nervous system function
- Producing DNA
Risk of Vitamin B12 deficiency
According to the National Institutes of Health, the following groups are among those most likely to be vitamin B12 deficient:
- Between 3% and 43% of community-dwelling older adults have vitamin B12 deficiency
- People with gastric atrophy, resulting in failure to produce intrinsic factor and malabsorption of dietary vitamin B12.
- Individuals with stomach and small intestine disorders — such as celiac disease and Crohn’s disease — may struggle to absorb enough vitamin B12 from food.
- Vegetarians and vegans at a higher risk of vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Exclusively breastfed infants of women who consume no animal products may have very limited reserves of vitamin B12 and can develop B12 deficiency.
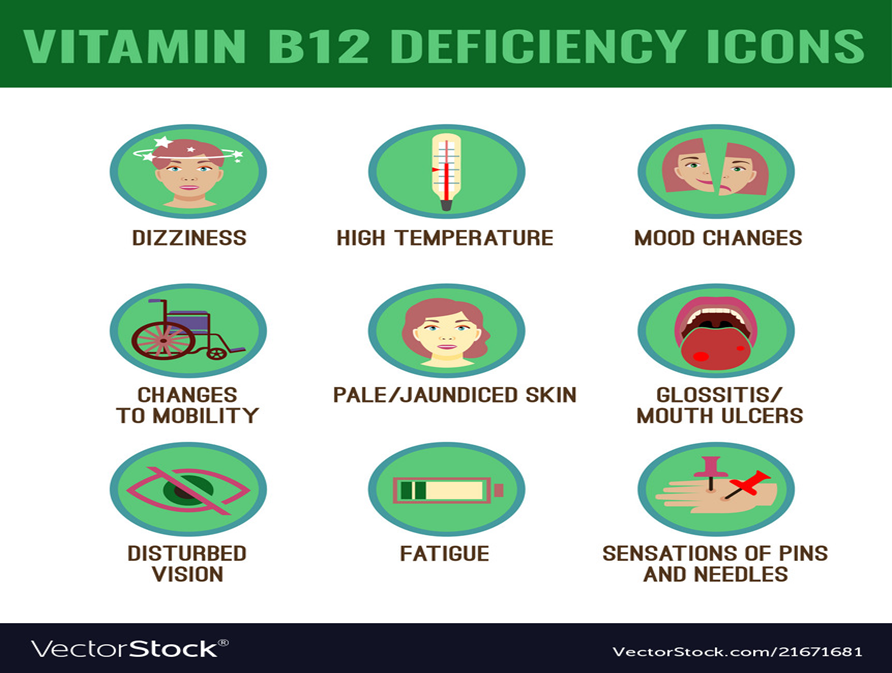
Signs of B12 deficiency
The best sources of vitamin B12
- Milk. Dairy and some non-dairy milks are fortified with vitamin B12.
- Fish. Many different types of fish are a great source of vitamin B12. Just one half of a cooked salmon fillet contains more than 200% of the daily value.
- Eggs. Both egg yolks and egg whites contain vitamin B12, with the yolk containing the majority. It’s important to eat the whole egg if you are aiming to increase your vitamin B12 intake.
- Fortified cereals. Just like milk, many healthy cereal options are fortified with B12 and other vitamins. These are particularly a great source of vitamin B12 for individuals who identify as vegan or vegetarian.
- Yogurt. Whether it be Greek yogurt or a variety of full-fat plain yogurt, these are a great source of vitamin B12.
- Beef. As a rule of thumb, leaner meats contain higher vitamin levels than the alternative. While beef is high in B12 and other vitamins, moderation is the key to seeing the most benefits and the least drawbacks of red meat.
- Liver and kidneys. Organ meats are very high in B12, but also contain larger amounts of cholesterol. If you choose to source vitamin B12 from liver and kidneys, be sure to do so in moderation.
- Clams. A mere 3.5-ounce serving of baby clams provides over 4,000% of vitamin B12’s daily nutritional value, they’re also a great source of protein, iron and antioxidants.
Vitamin B12 plays an essential role in many of your body’s major functions. Since your body doesn’t make vitamin B12 on its own, it’s important that you source it from animal-based foods or alternative supplements.

